VLSI engineers can hold various positions within the semiconductor industry, each with specific roles and responsibilities. Some common positions include:
1. VLSI Design Engineer: Responsible for designing and implementing digital or analog circuits using hardware description languages (HDLs) like Verilog or VHDL.
2. Physical Design Engineer: Focuses on the physical implementation of the chip, including floor planning, placement, routing, and timing closure.
3. Verification Engineer: Ensures that the designed chip functions correctly by creating testbenches, running simulations, and debugging potential issues.
4. Analog/Mixed-Signal Design Engineer: Specializes in designing circuits that integrate both analog and digital components, often found in systems-on-chip (SoCs).
5. RTL Engineer: Works on the Register Transfer Level (RTL) description of the design, which acts as a bridge between high-level design and physical implementation.
6. FPGA Engineer: Designs and implements digital circuits on Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) for prototyping or specialized applications.
7. DFT Engineer (Design for Testability): Focuses on designing chips with built-in test structures to ensure effective testing and fault detection during manufacturing.
8. CAD Engineer: Develops and maintains the design automation tools and flows used by VLSI designers for efficient chip development.
9. Applications Engineer: Supports customers by understanding their requirements and assisting them in using VLSI chips effectively in their applications.
These are just a few examples, and the roles and job titles in the semiconductor industry can vary across different companies and projects. VLSI engineers play a crucial role in the development of integrated circuits and are involved in various stages of chip design, verification, and production.
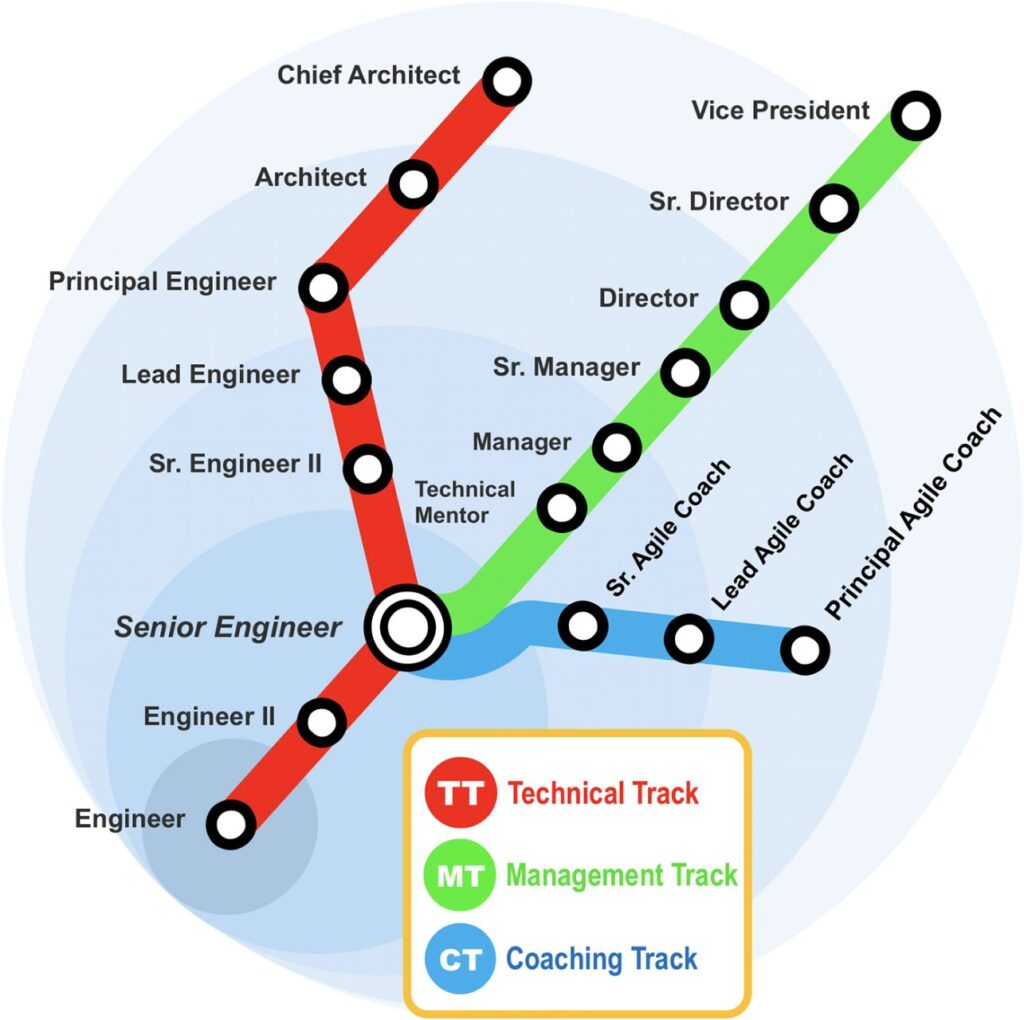
The Diagram below shows a different position based on different levels.
