When and how a TLP is allowed to transmit
- When and how a TLP is allowed to transmit
- 1 . Introduction
- 2 . Transmission Pre-Checks
- 3 . Credit Consumption Rules
- 4 . Transmission Decision Flow
- 5 . Example – Memory Write Transmission
- 6 . Example – Completion TLP
- 7 . Partial Transmission and Fragmentation
- 8 . Replay and Flow Control Interaction
- 9 . Credit Starvation and Link Stall
- 10 . Hardware Implementation Tips
- 11 . Verification and Debug
- NOTES
1 . Introduction
Once both link partners have exchanged and initialized their credits (as covered in Post 6.4), the transmitter can begin sending Transaction Layer Packets (TLPs).
But not every packet can leave immediately — each TLP must first pass a flow-control check.
These rules keep the link deterministic and guarantee that the receiver’s buffers will never overflow.
2 . Transmission Pre-Checks
Before a TLP is transmitted, the following conditions must hold for the selected Virtual Channel (VC):
- Header Credits Available → At least 1 header credit (H) for the TLP class.
- Data Credits Available → Enough data credits (D) to cover the payload length (if any).
- Replay Buffer Space → The Data Link Layer has space to store a copy for Ack/Nak replay.
- Link State = L0 → Flow control is active only in L0 and L0s.
- Ordering Rules Satisfied → If Relaxed Ordering = 0, dependencies must be honored.
If any check fails, transmission is deferred until credits return or conditions clear.
3 . Credit Consumption Rules
Each TLP type consumes credits from its respective pool:
| TLP Type | Header Credits Used | Data Credits Used |
| Memory Write (Posted) | PH | PD ( = payload DW count ) |
| Memory Read (Non-Posted) | NPH | 0 |
| I/O Write | NPH | NPD |
| Completion with Data | CPLH | CPLD ( payload DW count ) |
| Message with Data | PH | PD |
💡 Header = 1 credit per TLP, Data = payload length / 4 bytes (rounded up to nearest DW).
4 . Transmission Decision Flow
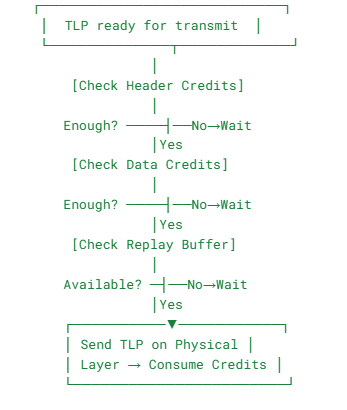
This logic runs per TLP queue (Posted, Non-Posted, Completion) and per VC.
5 . Example – Memory Write Transmission
Receiver advertised: PH = 8, PD = 32
Transmitter currently has: PH = 3, PD = 10
New TLP: Memory Write (Posted) with payload = 8 DW (32 bytes)
- Needs 1 PH + 8 PD credits.
- Transmitter has enough → TLP sent.
- Counters decrement → PH = 2, PD = 2.
- When receiver frees buffers → sends Flow Control Update DLLP → credits replenish.
If transmitter wants to send another Memory Write (12 DW payload) but PD = 2 → stall until PD ≥ 12.
6 . Example – Completion TLP
Endpoint → Root Complex
- CPLH = 5, CPLD = 16
- Completer ready to send CplD with 8 DW payload
→ Consumes 1 CPLH + 8 CPLD credits. - After send → CPLH = 4, CPLD = 8.
- Once Root Complex processes Completion → returns credits via DLLP.
7 . Partial Transmission and Fragmentation
If a payload exceeds the maximum available data credits, the TLP cannot be split by the link layer.
The Transaction Layer must wait until enough credits are available to send the entire packet.
❌ No fragmenting of TLPs allowed within the link.
✅ Credit updates ensure the whole packet fits in receiver buffers.
8 . Replay and Flow Control Interaction
- Data Link Layer retransmissions (replay) do not consume extra credits,
since credits represent receiver buffer space, not transmit attempts. - Credits are deducted only on first transmission.
- Replayed TLPs use copies from Replay Buffer without touching credit counters.
9 . Credit Starvation and Link Stall
If credits reach zero for a TLP class:
- Transmission for that class halts.
- Other TLP classes (with credits available) may continue.
- When Flow Control Update DLLP arrives → credits increase → link resumes.
This mechanism guarantees deadlock-free operation and efficient bandwidth sharing.
10 . Hardware Implementation Tips
In controller RTL:
- Maintain separate credit counters for each (VC, Class, Header/Data).
- Scheduler logic selects packets only if credits ≥ required value.
- Credits are atomically decremented on transmission.
- Flow Control Update DLLP handler increments counters.
if (credits_ok(type))
begin
send_tlp(tlp);
dec_credits(type, payload_dw);
end11 . Verification and Debug
Typical assertions:
assert(!(send_tlp && credits[type]==0))
else $fatal("TLP transmitted without credits!");
In protocol analyzer:
- Watch Flow Control DLLPs → confirm periodic updates.
- Check credit starvation points → identify backpressure.
- Confirm no packet loss even under heavy traffic.
NOTES
- Every TLP must pass a credit check before transmission.
- Header and Data credits are decremented on send and replenished via DLLPs.
- Separate pools per transaction class (P/NP/CPL) prevent deadlocks.
- Replay operations don’t affect credits.
- Flow Control and Transmission Rules together enable lossless, deterministic bandwidth in PCI Express.
